Before we talk about the database, let’s talk about data. What is data? And what it is for
What is Data
Data is the plural noun of datums. A single data is datum. Datum itself means “something given”. Datum can be anything. It can be a characteristic or a specification given to an observation object. Since data is a collection of datums, so we can say that data is a set of characteristics or specifications of the object of observation.
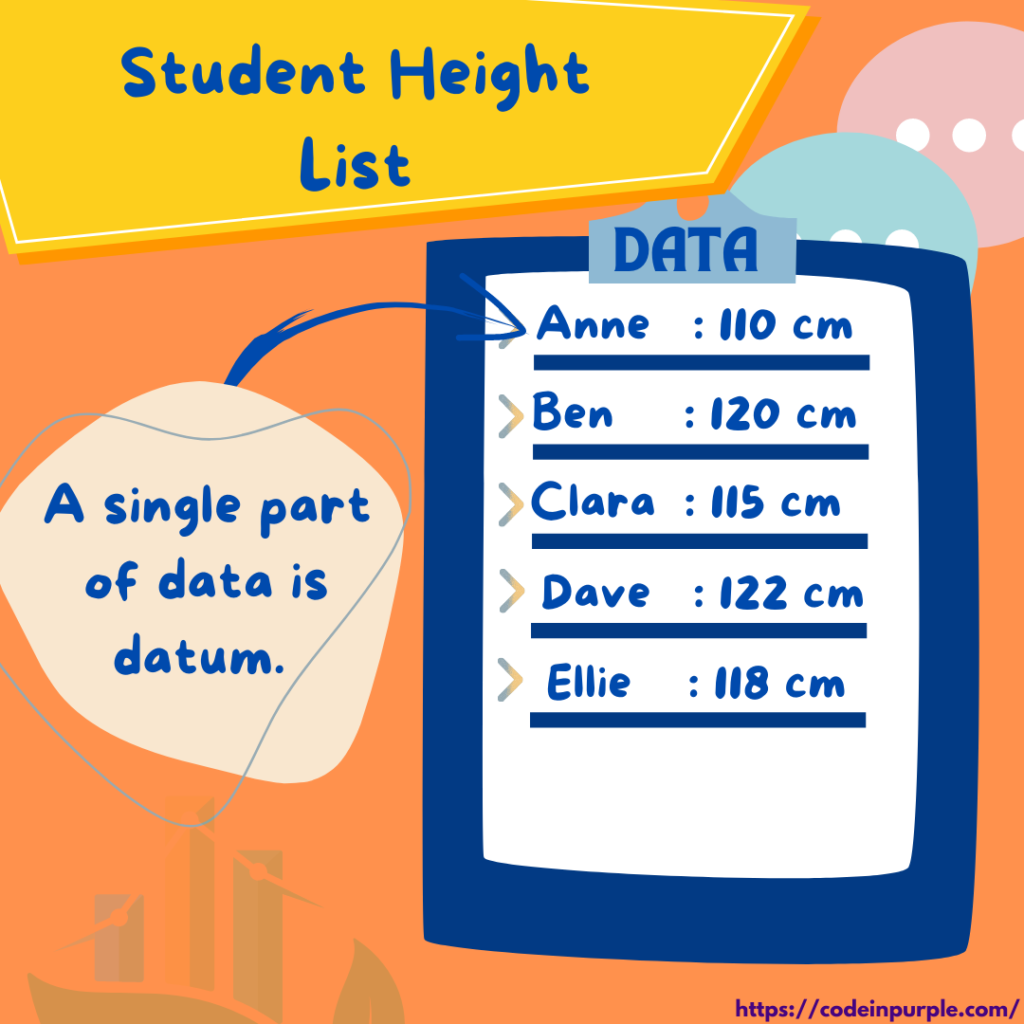
For example, let’s say we have a set of data on student height that consists of Anne, Ben, Clara, Dave, and Ellie’s height numbers. Then, the height list is data, and Anne’s height number is a datum, Brad’s height number is a datum, Charlie’s height number is a datum, and so on.
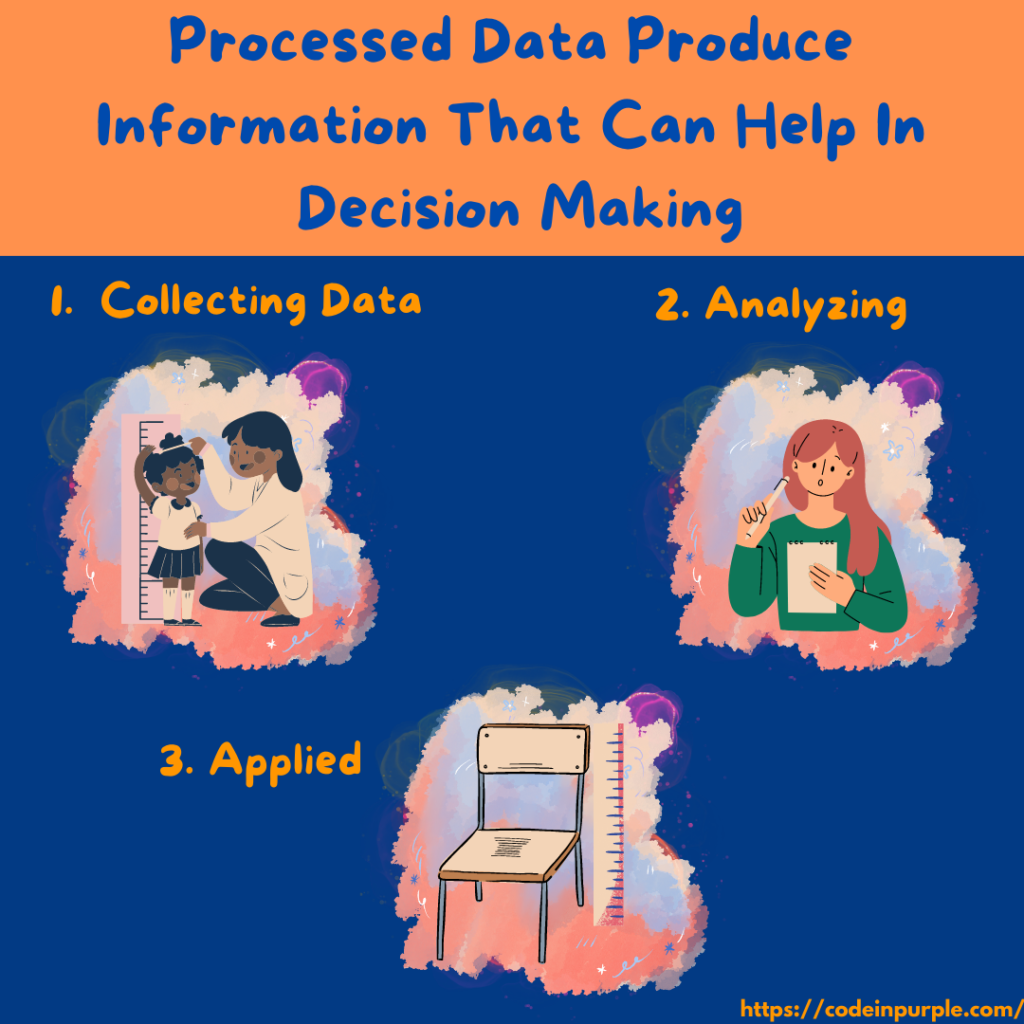
So, why do we need data? We need data to have information about a particular object or to make decisions about it. Data has no meaning until it is processed in a certain way and produces information that can be used/applied.
For Example, On the student height data, we can analyze and have information about the average height of the student so we can decide on a perfect standardized chair height that the student will use in the classroom.
Furthermore, let’s talk about databases.
What is a Database?
A database is structured and organized related data. It is intentionally designed to make it easier to store, access, manage, update, observe, analyze, and modify. In computer programming terms, it is usually managed by a “database management system” (DBMS) software, such as MySQL, Oracle, MongoDB, and Microsoft SQL Server.
There are a few database types based on the distribution method, where the data is located, and how the data model is stored and managed.
Type of Database
1. Based On How It Located
A. Distributed
The distributed database has two or multiple files stored in different places. This technique will benefit database performance because the data distribution is arranged according to the most demanding location.
B. Centered
The centered database is stored in one location. This type is easier to manage and maintain because we can focus only on one location. However, if the data traffic is high, it might cause a bottleneck.
2. Based On Where It Located
A. On-Premise / Local
The on-premise is located in a local drive or local area network. It is accessed, managed & maintained in private. It also has its own infrastructure. Local databases are usually only accessible to specific and limited circles.
B. Public Cloud
Using a Public cloud means using public infrastructure to build a database ecosystem in the cloud platform that can be accessed using the internet. The infrastructure like server and storage is owned by a third party and is shared with other cloud tenants. Even though the infrastructure is shared, the data is still secure and can only be managed by its owner or anyone that is permitted to access by the owner.
C. Private Cloud
Using a Public cloud means using public infrastructure to build a database ecosystem in the cloud platform that can be accessed using the internet. The infrastructure, like server and storage, is owned by a third party and is shared with other cloud tenants. Even though the infrastructure is shared, the data is still secure and can only be managed by its owner or anyone permitted access by the owner.
D. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud environments combine On-Premise, Private Cloud, and Public Cloud. The data is allowed to move within those environments
3. Based On The Data Modeling
A. Relational
This is the most popular scheme to this day. Relational modeling is arranged based on the relationship of each data item, and the data is stored using a table format.
B. Object-Oriented
The object-oriented modeling can handle complex data. The data is stored as an object and similar/related objects are collected in a class.
C. Hierarchical
This is the most traditional scheme of the database. The structure looks like a tree, and it is a parent-child form.
D. NoSQL
NoSQL is a non-relational-based database. It has a flexible schema and horizontal scaling. There are some popular types of NoSQL databases:
- Graph
Graph model stores data in nodes. A node is connected to another node that has a specific relationship. - Document Based
Document-based is a non-relational and flexible database. It is stored in document formats like JSON, BSON, or XML.
- Key Value Store
The key value is like dictionaries containing objects with many fields filled with data. The data can be accessed using a unique identifier key. - Column-Oriented
This modeling stores data in columns instead of rows to create efficient access to data.
Infrastructure and Environments
To Build a database, we need to provide its infrastructure and environments like:
1. Hardware
Hardware is a physical machine that meets the minimum requirements to store and run all needed systems.
2. Software
There are two kinds of software: Operating System Software and Application Software. Operating System software is required to run Application software that will manage the database. And the application software is known as DBMS (Database Management System).
3. Data
Data is the raw material of the database. Without enough data, a database can not be analyzed or produced any information to help make a decision.
4. Data Access Language
Data Access Language is a set of command languages that DBMS can understand. This command usually includes instructions to store, retrieve, update, delete, and sort data.
5. Procedure
The procedure is the rule applied to a database. This rule helps to run and manage the database.
The Challenges
Due to its importance, Setting up & managing a database can be challenging. Some common challenges are:
1. Data Security
Data is a valuable asset. It can contain secret information. The database needs a proper security system to protect it from unauthorized access.
2. Data Integrity
The database collects data from many resources, and it takes work to ensure that the data source presents valid data.
3. Performance
Over time, the data will grow larger; for this reason, it is necessary to upgrade the infrastructure and environment that is more adequate than before. System updates for both software and hardware, are required to maintain or improve performance.
4. Integration
Sometimes databases need to be integrated with each other, for example, integrating login authentication with Google or social media API. Related data must exist in the database so that the integrated data can be analyzed and used correctly.
References:
– https://www.mongodb.com/databases/what-is-an-object-oriented-database
– https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/hierarchical-model-in-dbms/
– https://www.dictionary.com/browse/datum
– https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatamanagement/definition/database
– https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database
– https://www.guru99.com/introduction-to-database-sql.html
– https://www.javatpoint.com/what-is-database
– https://www.oracle.com/database/what-is-database/
– https://docwiki.embarcadero.com/RADStudio/Sydney/en/Types_of_Databases











One Comment
Comments are closed.